Route Alignment in Train Control
In the realm of train control systems, route alignment plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of trains. Proper route alignment ensures that trains follow their intended path, avoiding conflicts and potential accidents. This article aims to shed light on the basic rules governing route alignment in the train control process.
Understanding Track Layout
The first fundamental rule of route alignment is to have a comprehensive understanding of the track layout. This includes studying the track configuration, switch locations, signals, and interlocking systems. It is essential to know the various track sections, their connections, and any potential limitations or restrictions along the route.
Establishing Train Movements
Route alignment requires a clear understanding of the train movements. This involves determining the intended path for each train, including its departure and destination points. By establishing the train movements, the route alignment process can be tailored to ensure that trains can move safely and efficiently from one point to another.
Respecting Signal Indications
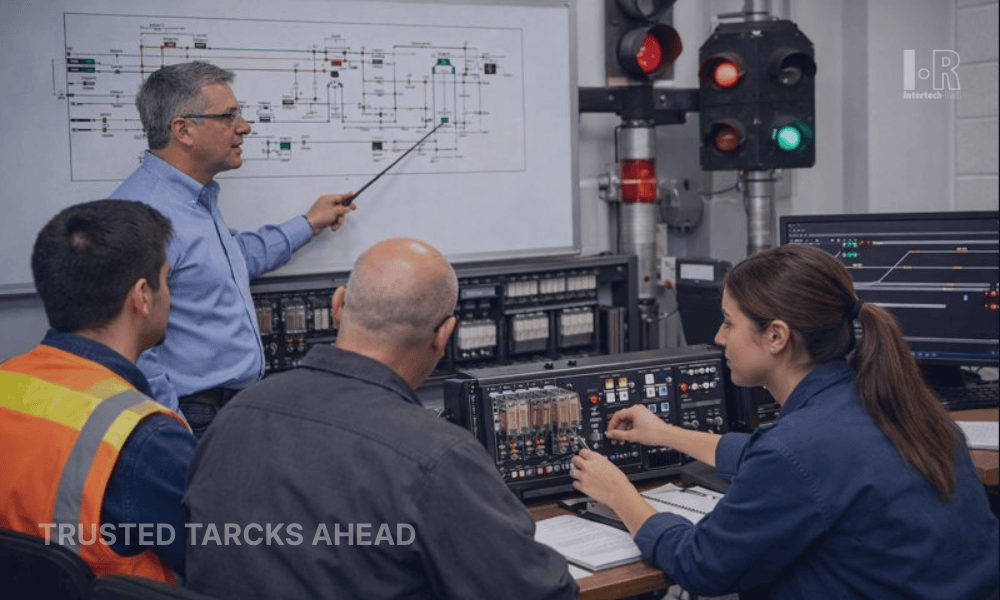
Signals are critical components of the train control process, providing essential information to train operators. Following signal indications is a vital rule for route alignment. Operators must adhere to the instructions conveyed by signals, which indicate whether a train should proceed, slow down, stop, or change tracks. Failing to respect signal indications can lead to accidents or disruptions in train operations.Parágrafo Novo
Coordinating with Switches and Interlockings
Switches and
interlocking systems allow for the diversion of trains from one track to another. Coordination between route alignment and these systems is vital to ensure safe and efficient train movements. Switches must be aligned correctly to direct trains onto the desired tracks, while interlocking systems ensure that conflicting routes cannot be set simultaneously. Proper coordination minimizes the
risk of collisions or
derailments.
Considering Train Characteristics
Different trains have varying characteristics, such as length, speed capabilities, and braking distances. These characteristics must be taken into account during the route alignment process. Aligning routes suitable for the specific train type and its capabilities ensures that trains can navigate the tracks safely and maintain optimal operational efficiency.
Adhering to Timetable and Traffic Control
In a busy rail network, maintaining a consistent timetable and traffic control is essential. Route alignment should prioritize efficient movement while adhering to the schedule and minimizing conflicts with other trains. This requires careful coordination with the train dispatching system to allocate appropriate time slots and routes to different trains, ensuring smooth operations.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
To ensure the integrity of the route alignment system, regular maintenance and inspection of tracks, switches, and signals are necessary. Any defects or malfunctions in the infrastructure must be promptly addressed to avoid compromising the safe movement of trains. Maintenance crews should perform routine inspections and make necessary repairs or replacements as required.
Route alignment is a critical aspect of the train control process, influencing the safety, efficiency, and reliability of rail operations. Understanding the track layout, respecting signal indications, coordinating with switches and interlockings, considering train characteristics, adhering to timetables and traffic control, and conducting regular maintenance are essential rules that govern route alignment. By following these rules, railway operators can ensure the smooth and secure movement of trains, contributing to a robust and reliable train control system.